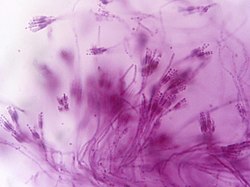
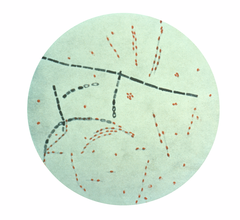
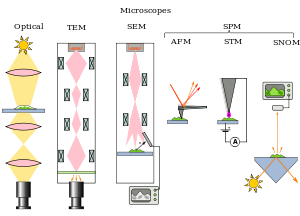
This week (week 3), in microbiology class I identified the parts of a basic microscope. Besides, I described the principle of light, phase-contrast, fluorescence and electron microscope. Furthermore, I have to select suitable microscope for relevant usage and recognized images produces from different microscope.
MICROSCOPE PARTS

TYPES OF MICROSCOPE:
OPTICAL
- dark field
- bright field
- fluorescence microscopy
- phase-contrast microscopy
ELECTRON
- scanning electron microscope
- transmission electron microscope
- environmental scanning electron microscope
SCANNING PROBE
- atomic force
- scanning tunneling
- scanning near-field optical microscope
SCANNING ACOUSTIC MICROSCOPE
PROKARYOTE
For Thursday Class, Dr Wan asked every student to make online mind map and submit before class. This mind map was very interesting and useful as can put video, picture and article, so student can study based on this mind map. It easy to understand and remember. Besides. during class, Dr Wan asked everybody to draw a mind map on the white board. This part was very funny as everyone busy to write everything about prokaryote so there have same answer. At end of class, Dr wan asked students to make a quizlet about prokaryote. There we did some word and explanation than shared it with everybody. We also did a test based on what we had done in the quizlet.
In this week or this topics, I very enjoy and happy with the class as I'm not sleepy in the class but I very concentrate with the learning. This Microbiology class was awesome.